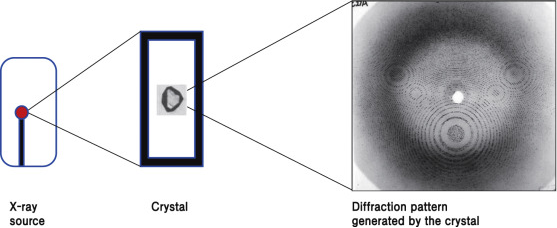
X-ray crystallography is a technique based on X-ray diffraction used to determine the positioning of atoms in a crystal. In a crystal structure atoms or molecules are arranged in space. There is diffraction of the beam when it strikes on a crystal. The angle of diffraction and intensity of beams help us to predict the 3D structure of the crystal. When a single particle strikes, the incident beam is scattered in all directions uniformly. Material regularity is behind the nature of diffraction of beams.
There is Bragg’s law which gives the relationship of angle diffracted of the X-ray beam at a particular wavelength in crystal surface. The Bragg’s law was discovered by Sir William H.Bragg and Sir W. Lawrence Bragg.
nλ=2dsinΘ
n= integer
λ= wavelength of X-ray
d= space between planes
Θ= angle between the incident ray and scattering planes
X-ray is used as these are of shorter wavelength 0.01 and 10nm so, they have the same magnitude as there is the distance between atoms in a crystal. X-ray they constructively interfere when the incident beam is scattered producing the diffracted beam. The pattern of diffraction is accounted on the photographic plate pattern which helps to find out the nature of lattice i.e. the arrangement of atoms or molecules in the crystal.